Committees
The Pan-African Parliament has eleven Permanent Committees whose functions are aligned to those of the African Union Commissions. Each Committee has a maximum number of thirty Members with regional and gender representation (Rule 22 (5)) excluding the Committee on Audit and Public Accounts which has a maximum number of fifteen Members.
Members are designated to committees by the five (5) Regional Caucuses, including new members who have gone through the verification exercise by the Committee on Rules, Discipline and Privileges to ensure that the procedure and conditions for designation by their National Parliaments are met. The Permanent Committees meet twice a year (March and August) for statutory meetings and can meet more often during parliamentary sessions or for non-statutory meetings when the need arises.
The Role and Functions of Permanent Committees
The Committees are the engine House of any Parliament. The creation of PAP Permanent Committees was, therefore, an important move by the Pan-African Parliament to ensure in-depth analysis on topical and emerging issues facing Africa. The Committees enable Parliament to perform its core oversight, advisory and consultative functions. Further, such an arrangement allows the Parliament to perform several functions simultaneously and provide required detailed investigation on matters of concern.
Rule 26 of the Pan-African Parliament Rules of Procedure lists the specific functions of the Committees concerning their purview as depicted in their title as:
- Oversight on the development and harmonization of policies of the African Union and the Member States.
- To examine the review of the protocol and treaties of the Union.
- Oversight on relevant organs or institutions of the African Union.
- To promote the development and implementation of African Union Programs.
- Investigate and report to the Plenary, findings on matters to which they have been assigned.
The Committees implement programs and projects aligned with the PAP Strategic plan 2018-2023, drafted in consideration of the vision of the Parliament, Agenda 2063, AU programs and theme of the year. This implies that issues that the Committees investigates, debates on and reports to the Plenary are relevant towards the achievement of the Africa Union Agenda. This allows for synergy and consistency with the work of the African Union and its Commission. Additionally, with the mapping of the agenda 2063 exercise carried out by the PAP Permanent Committees, the Committees have identified their role in implementing the AU Vision and its flagship project also cognizant of addressing emerging matters.
Based on the program of the Permanent Committees implemented, recommendations are made from their findings in the reports which are presented to the Plenary. The recommendations elaborate expectations from various stakeholders, which could be internal or external, to address the matter under consideration. The recommendations are adopted by the Plenary if there is collective agreement on the proposal. Adopted recommendations form part of the Report of the President of the PAP that is considered by the Assembly of Heads of State and Government. It is expected that these plenary recommendations inform the formulation of AU policies and decisions.
The eleven PAP Permanent Committees
- Committee on Education, Culture, Tourism and Human Resources: It assists the Parliament with policy development and implementation of programmes on issues of access to education, promotion of culture and tourism, and human resource development.
- Committee on Cooperation, International Relations and Conflict Resolution: The Committee considers policy issues on international cooperation and international relations on behalf of the Parliament and AU. It also deals with conventions and protocols linking the Parliament with regional and international institutions. The Committee examines revisions of AU protocols and treaties and provides assistance to the Parliament in its conflict prevention and resolution efforts.
- Committee on Gender, Family, Youth and People with Disabilities: Considers issues relating to the promotion of gender equality and assists the Parliament to oversee the development of AU policies and activities relating to family, youth and people with disabilities.
- Committee on Monetary and Financial Affairs: Examines the Parliamentary budget draft estimates. It also examines the AU budget and makes recommendations. The Committee reports to the Parliament on any problems involved in the implementation of the annual AU and PAP budgets. It advises the Parliament on economic, monetary and investment policies.
- Committee on Trade, Customs and Immigration Matters: Deals with matters relating to the development of policy for cross-border, regional and continental concerns within the areas of trade (primarily external trade), customs and immigration. It assists the Parliament to oversee relevant organs or institutions and AU policies relating to trade.
- Committee on Health, Labour and Social Affairs: Works to support the implementation of social development, labour and health policies and programmes throughout the AU, including through regional and international cooperation strategies.
- Committee on Transport, Industry, Communications, Energy, Science and Technology: .Assists the Parliament to oversee the development and implementation of AU policies relating to transport, communication, energy, science and technology, and industry.
- Committee on Rules, Privileges and Discipline: Assists the Parliament Bureau to interpret and apply the PAP Rules of Procedure, as well as matters relating to privileges and discipline. It considers requests for ‘waivers of immunity’ submitted under the Rules of Procedure and examines cases of indiscipline. The Committee also considers proposals for amending the Rules of Procedure.
- Committee on Justice and Human Rights: Assists the Parliament in its role of harmonising and coordinating Member States’ laws. It advocates for respect within the AU of the principles of freedom, civil liberties, justice, human and peoples’ rights, and fundamental rights.
- Committee on Rural Economy, Agriculture, Natural Resources and Environment: Considers the development of common regional and continental policies in the agricultural sector. It provides assistance to the Parliament to oversee and promote the harmonisation of policies for rural and agricultural development as well as the AU’s natural resources and environmental policies.
- Committee on Audit and Public Accounts (CAPA): Considers internal and external audit reports on the PAP, and the Board of External Auditors’ reports on the AU, and recommends measures for effective implementation of the recommendations.
Leadership of Permanent Committees
Hon. Sakata Tawab Garry
Rural Economy, Agriculture, Natural Resources and Environment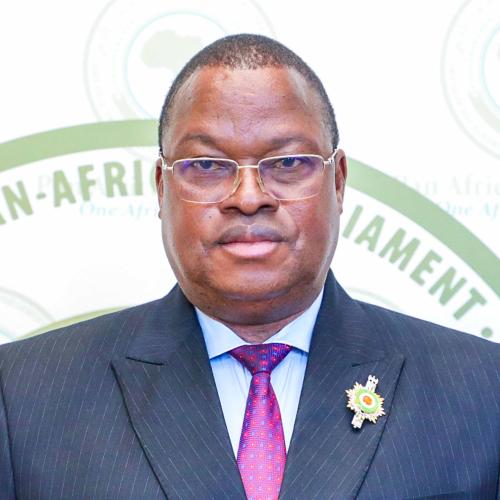
Hon. Kouadio Kouakou Bertin
Education, Culture, Tourism and Human Resources
Hon. Thérèse Faye
Monetary and Financial Affairs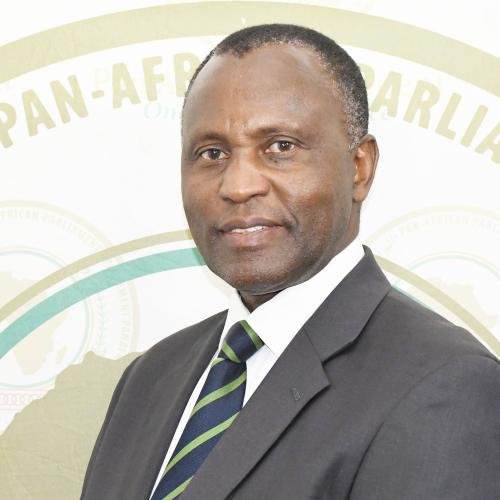
Hon. Sen. John Bonds Bideri
Trade, Customs, and Immigration matters- PK
Hon. Prof. Margaret Kamar
Health, Labour and Social Affairs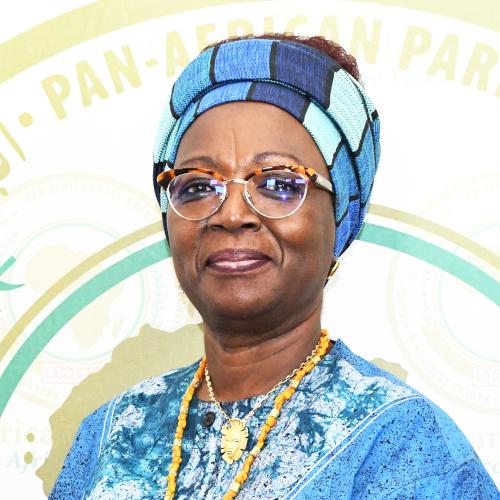 
Hon. Dao Gabala Mariam
Gender, Family, Youth and People with Disability- JN
Hon. Jean Marie Nibirantije
Justice and Human Rights - Rules, Privileges and Discipline

Hon. Behdja Lammali
Transport, Industry, Communication, Energy, Science and Technology
Hon. Dr. Eng. Sherif El Gabaly
Cooperation, International Relations and Conflict Resolution
Hon. Miles Sampa
Audit and Public Accounts





